Glaucoma Examination
Glaucoma has become the world’s second leading cause of blindness, after cataract.
Although it is common, most patients are not aware of having it until vision has become bad and visual field defective. Because of this lack of symptoms in the early stages, glaucoma is sometimes called ‘the silent thief of vision’. It has been estimated that there is about 50% of undiagnosed glaucoma. Routine eye examination is surely most important in the detection and prevention of the disease from progressing to a point of irreversible vision loss.
Glaucoma is a multifactorial condition with characteristic optic nerve damage and visual field defects.
Risk factors:
- Age
- Family history/genetics
- Race
- Intraocular pressure (IOP)
- Myopia
- Diabetes
Glaucoma examination includes the following:
- Complaints and history taking
- Visual function tests
- IOP measurement
- Corneal thickness measurement
- Assessment of the anterior segment, anterior chamber and angle
- Visual field test
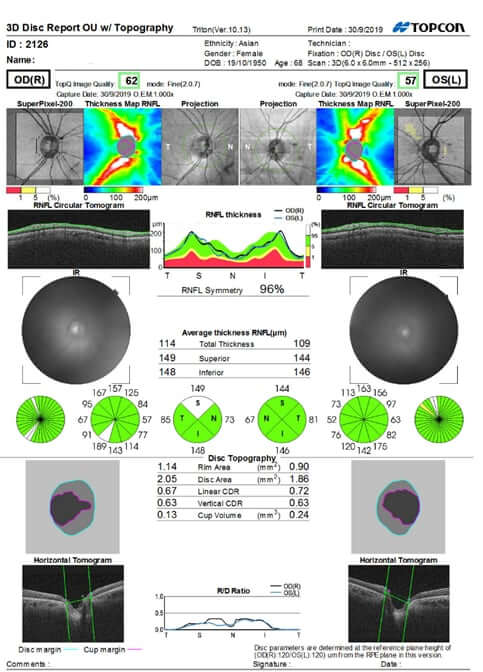
- Evaluation of the Optic Nerve
- Fundus photography
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
- Analysis of findings and recommendation